THE 3Rs PRINCIPLES OF ANIMAL USE IN RESEARCH
The 3Rs principles of animal use in research resulted from a study commissioned by the Universities Federation for Animal Welfare in the 1950s. They were formulated by Russell and Burch in 19591, and are now internationally accepted as a framework to eliminate unnecessary harm to animals used in research.
Replacement
Replacement refers to methods and approaches that replace the use of animals in experiments. Sometimes, using invertebrates instead of vertebrates is also considered (partial) replacement.
Reduction
Reduction refers to techniques that aim to minimise the number of animals used in each study while maintaining a sound statistical design. Using an excessive number of animals incurs an unnecessary ethical cost, but using too few animals may yield invalid results and waste the animals involved. Reduction can be achieved by maximizing the information gathered from each animal or by promoting data and resource sharing among researchers.
Refinement
Refinement refers to methods that minimize pain, suffering, or discomfort.
BENEFITS OF IMPLEMENTING THE 3Rs PRINCIPLES
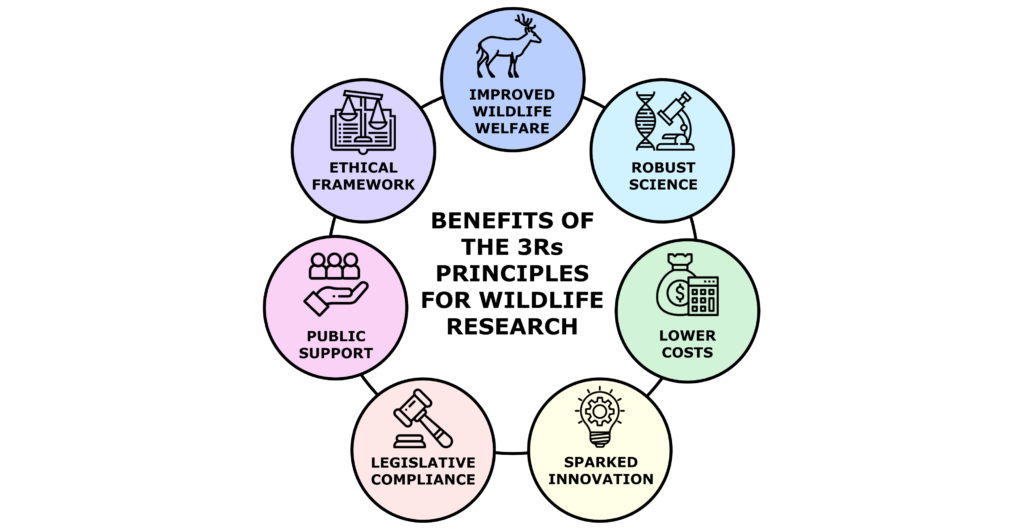
There are several advantages associated with the implementation of the 3Rs principles in ecological research on wildlife. The first and most obvious benefit is improved animal welfare. Additionally, scientific results can be compromised if they are affected by the stress or injuries caused to animals through invasive research methods2. Consequently, implementing the 3Rs principles in wildlife research is crucial not only for the well-being of the animals under study but also to ensure robust and reliable science3. The 3Rs principles can also serve as a practical ethical tool. Ecological studies and research on wildlife typically receive public support, as both scientists and the general public consider the conservation of species and the associated ecosystem services they provide to be crucial for our long-term survival. However, research that has the potential to harm animals may encounter public outrage4. Nowadays, the 3Rs principles are an integral part of legislation in many countries worldwide. For instance, within the European Union, the 3Rs are implemented in the EU Directive 63/2010, making their implementation a legal requirement. Other benefits include the cost-effectiveness of some non-invasive research methods5 and the development of innovative approaches in wildlife research6, 7.